How to test an alternator with a multimeter can be easy if you just know the proper way to do it. Just follow the simple procedure mentioned.
An automobile has many electrical devices, such as the starting system, lights, radio, etc. These devices are operated by the electric current supplied from the battery and alternator. The amount of power generated depends on the alternator specification and engine speed. Power generation is automatically controlled according to the battery condition and the car’s electrical consumption (load) at a specific time. Generally, when the engine runs at idle the battery discharges, and as the engine speed increases the battery is charged by the alternator.
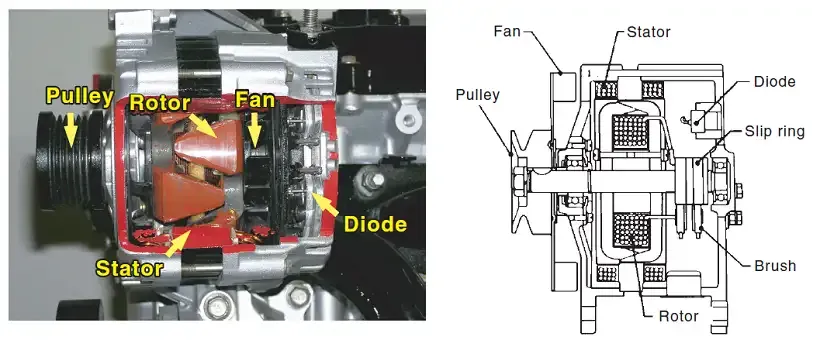
Parts of a car alternator and function
• Rotor.The rotor is the one that rotates (that’s why it is called rotor), it is simply a rotating magnetic field. The rotor generates magnetism as the current flows through it. When the rotor turns, electricity is generated in the stator. The voltage for the rotor is supplied by the voltage regulator through the brushes and the slip rings.
• Stator (armature coil).The stator is called “stator” because it is stationary, the stator is attached to the body with three separate windings connected to the external circuit through the rectifier bridges consist of six diodes. As the rotor turns, the magnetic force passing through the stator changes, and this change causes an electric current to flow through the stator coil.
• Diode assembly. The diodes are used to rectify the alternating current (AC) generated in the stator to obtain direct current (DC).
• Brush and slip ring. Electricity is supplied to the rotating rotor through these parts.
• Fan. The diode has a comparatively low heat resistance and coil resistance decreases when cooled, so a fan is used to cool the diodes and coils in the alternator. The fan also cools the alternator with a built-in IC regulator.
• Pulley. The power from the engine is transmitted through the V-belt and the pulley to the rotor.
How to test car alternator
Before conducting to test car alternator, make sure that the battery is fully charged. A 30-volt voltmeter and suitable test probes are necessary for the test. The alternator can be checked easily by referring to the Inspection Table.
Check Alternator Belt and Terminal S Fuse
Check the alternator belt tension before starting the engine. Check the fuse of terminal S. When the ignition switch is ON, measure the voltage at terminal S with the terminal S connector disconnected. If it is 12V, the fuse and the wire from the fuse to terminal S are normal.
Measure the voltage between the terminal L, S, and the ground. The condition of the car must be, the engine is stopped, the ignition switch shall be at ON position, the connector S shall be disconnected.
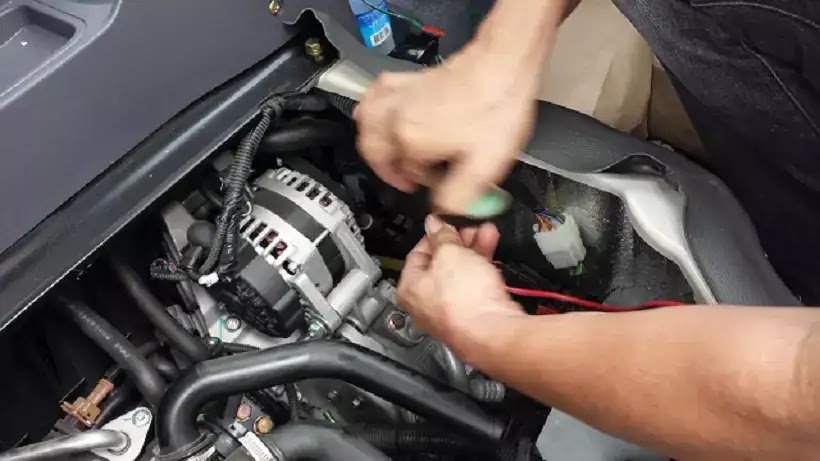
How to Test an Alternator with Multimeter
To test an alternator with a multimeter measure the output voltage at alternator terminal B. Test an alternator 0utput voltage, measure the output voltage at alternator terminal B. The battery voltage is usually about 12V. To charge the battery, a higher voltage (about 13V to 15V) is required. If the alternator output voltage is 13V or less, the battery continues discharging, thus the battery runs down.
If the voltage is 13V or less, the alternator output is NG. As it is OK when the alternator output is 13V to 15V, measure the voltage at the positive terminal of the battery. If the battery voltage is 13V or less, there is a malfunction at terminal B or the wire harness. Check the connection status. Vehicles with the “Variable voltage generation system” have different voltage values.
How to Test an Alternator by Disconnecting Battery
How to test if your alternator is bad by simply disconnecting the battery? To test an alternator by disconnecting the battery, follow this simple step.
(1) Park the car on level ground, away from traffic, and engage the parking brake. Do not turn off the engine, just let the engine running.
(2) Now open the hood of the car, disconnect the battery, and observed if the engine will remain running. If the engine remains running then the alternator is fine. However, if the engine stopped after disconnecting the battery, then there is a problem with the alternator.
Inspection and disassembly of the alternator
Disassemble the alternator and inspect the internal part. Check each part for any problem.
(1) Remove the front cover through bolts.
(2) Before removing the front cover, warm the rear cover with a soldering iron as shown in the illustration. The bearing at the rear end of the rotor can be easily removed from the rear cover. Excessive heating may damage the IC regulator or the diode. Do not use a dryer.
(3) By tapping the flange of the front cover with a plastic hammer, the front cover and the rotor can be removed as an assembly from the stator and the rear cover.
(4) Loosen the screw behind the rear cover, the screw of the IC regulator, and the nut of terminal B. Remove the stator assembly from the rear cover and check the following items.
4.1 Brush
Inspect the brush condition of the alternator shown by the arrow. Check if the brush moves smoothly. If it doesn't, clean the brush. Is the brush worn? If it is worn, replace it. Remove the brush from the holder on the IC regulator assembly with a soldering iron as shown in the illustration.
In the illustration, the upper brush has been worn after being used for 130,000 km. The lower brush is a new one, and the arrow shows the wear limit line.
4.2 Test the alternator rotor
Test the alternator rotor using a digital voltmeter. Measure the resistance of the rotor at the slip rings. If it is not within the specified value, replace the rotor.
4.3 Insulation Test
Check the insulation resistance. Measure the resistance between the coil (slip ring) and the rotor body. Replace the rotor if continuity exists.
4.4 Slip Ring
Check the wear of the slip ring. If it is not within the specified value, replace the rotor.
4.5 Stator
Remove the diode assembly and check the following items.
Continuity test
No continuity: Replace the stator.
Assemble alternator and diagnose alternator output
1. Install the stator coil assembly on the rear cover and push away the brush with a finger until it is not visible as shown in the photo.
2. While pushing away the brush with a finger, insert a pin of appropriate thickness into the pinhole near the bearing boss at the back of the rear cover, to hold the brushes.
3. The brushes are held by the pin so that the rotor can be easily installed. Do not forget to remove the pin after assembly. Be sure to check the bearing. If unusual noise is heard. After assembly, make sure that the pulley turns smoothly and quietly.
How to Test Alternator Diode Rectifier
To diagnose the diode for the alternator, the diode can be diagnosed by measuring the output waveform as well. For measurement, the oscilloscope is used.
Measure the waveform with 0.1V/div and 2ms/div display mode. Since the alternator has 3-phase AC full-wave rectification, 6 peaks are displayed for one cycle of the alternator output.
If the diode(s) of the rectification circuit is (are) damaged, the waveform becomes unusual. If the output waveform is distorted, it becomes electric noise that affects the audio system and other electronic devices.
When diagnosing the alternator, measure the waveform. If an error is found, replace the diode. If the waveform is normal and the output voltage is excessively high, replace the IC regulator. If the output is low, check the brush, rotor, and stator.
Want more videos all about auto?
Subscribe to our YouTube channel! » Cartech Home