Car overheating when accelerating is a common problem that can lead to serious damage if not addressed promptly. The issue of "car overheating when accelerating" is something that many drivers may experience, but not everyone understands why it happens or how to prevent it. This article will dive into the causes of this problem, offer some preventative measures, and suggest solutions that will help keep your vehicle running smoothly.
👉 Understanding the Basics of Car Overheating
Before we delve into why your car might be overheating when you accelerate, it's important to understand what happens during overheating. Overheating occurs when the engine temperature exceeds the normal operating range. The engine's cooling system is designed to dissipate heat, but when it fails, the temperature rises, potentially causing severe damage to the engine and other components.
👉 Why Does a Car Overheat When Accelerating?
Several factors can cause a car to overheat when accelerating. Understanding these causes can help you identify the problem early and take the necessary steps to prevent further damage.
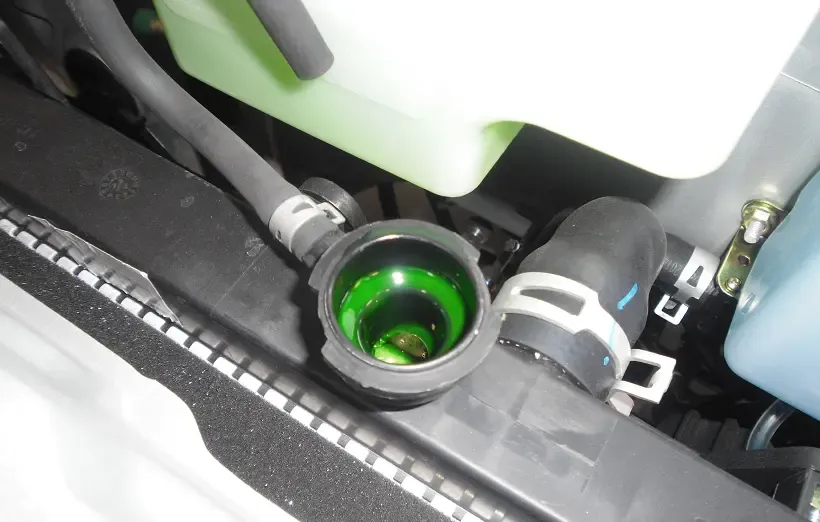
1. Insufficient Coolant Levels. Coolant is essential for regulating the engine's temperature. If the coolant level is low, there won't be enough fluid to absorb the engine's heat, leading to overheating. This problem can become more pronounced when accelerating, as the engine works harder and generates more heat. Always check your coolant levels regularly and top up if necessary to avoid this issue.
2. Faulty Thermostat. The thermostat controls the flow of coolant through the engine. If it's stuck in the closed position, the coolant won't circulate properly, causing the engine to overheat. During acceleration, the demand on the engine increases, and if the thermostat isn't functioning correctly, the temperature can rise quickly.
3. Clogged Radiator. The radiator plays a crucial role in cooling the engine. Over time, debris and dirt can accumulate, clogging the radiator and reducing its efficiency. A clogged radiator can't dissipate heat effectively, which can lead to overheating, especially when you're accelerating. Regular radiator maintenance is essential to prevent this issue.
4. Water Pump Failure. The water pump is responsible for circulating coolant throughout the engine. If the water pump is failing, the coolant won't move efficiently, leading to overheating. Acceleration puts extra strain on the engine, making the problem more noticeable. A faulty water pump should be replaced immediately to prevent severe engine damage.
5. Leaking Coolant System. Leaks in the cooling system can lead to a loss of coolant, which in turn causes overheating. Common leak points include the radiator, hoses, and water pump. If you notice a drop in coolant levels or see coolant under your car, it's crucial to address the leak immediately to avoid overheating, especially when accelerating.
6. Blocked or Broken Cooling Fans. Cooling fans help maintain the engine's temperature by drawing air through the radiator. If the fans are broken or blocked, the engine may overheat, particularly when accelerating. The extra heat generated during acceleration requires effective cooling, and without functioning fans, the temperature can rise rapidly.
7. Head Gasket Failure. The head gasket seals the engine's combustion chambers and prevents coolant from mixing with engine oil. If the head gasket fails, it can lead to overheating, especially under the strain of acceleration. This is a serious issue that requires immediate attention, as a blown head gasket can cause extensive engine damage.
👉 Preventing Car Overheating When Accelerating
Prevention is always better than cure. Regular maintenance and careful driving can help you avoid the problem of a car overheating when accelerating.
1. Regular Coolant Checks. Ensure that your coolant levels are always adequate. Check the coolant reservoir regularly and top it up as needed. Also, consider flushing the coolant system periodically to remove any contaminants that might impede its efficiency.
2. Thermostat Maintenance. Replace the thermostat according to the manufacturer's recommendations or if you notice any signs of it malfunctioning. A faulty thermostat can lead to serious overheating issues, so don't ignore any warning signs.
3. Radiator Care. Keep your radiator clean and free of debris. Consider having it professionally flushed and cleaned periodically. If you notice any signs of clogging, such as the engine running hotter than usual, address it immediately.
4. Water Pump Inspection. Regularly inspect the water pump for signs of wear or failure. If your car is overheating when accelerating and you've ruled out other issues, the water pump might be the culprit. Replace it if necessary.
5. Check for Leaks. Inspect the cooling system for leaks regularly. Look for signs of coolant under your car or on engine components. If you find a leak, have it repaired as soon as possible to prevent overheating.
6. Cooling Fan Functionality. Ensure that the cooling fans are functioning correctly. Listen for the fan when the engine is running hot, and check for any obstructions that might be preventing it from operating effectively.
7. Head Gasket Health. Be mindful of the symptoms of a failing head gasket, such as white smoke from the exhaust, coolant loss, or milky oil. If you suspect a head gasket issue, seek professional assistance immediately to avoid costly engine repairs.
👉 What to Do if Your Car Overheats When Accelerating
If you find yourself in a situation where your car is overheating when accelerating, it's crucial to act quickly to prevent further damage.
1. Pull Over Safely. If you notice the temperature gauge rising rapidly or steam coming from under the hood, pull over to a safe location as soon as possible. Continuing to drive could cause severe engine damage.
2. Turn Off the Engine. Turn off the engine to prevent it from overheating further. Open the hood carefully to allow the heat to dissipate, but be cautious of hot steam or fluids.
3. Check Coolant Levels. If the engine has cooled down, check the coolant levels. If they're low, add coolant if you have it on hand. Be sure to wait until the engine has cooled sufficiently before removing the radiator cap to avoid burns.
4. Call for Assistance. If you're unable to resolve the issue on your own, or if the car continues to overheat, it's best to call for professional assistance. Driving with an overheating engine can lead to catastrophic failure, so it's better to be safe than sorry.
💬 Final Thoughts"Car overheating when accelerating" is a problem that no driver wants to face, but understanding the causes and solutions can help you prevent it from happening. By keeping up with regular maintenance, checking your coolant levels, and being aware of the signs of trouble, you can keep your car running smoothly and avoid the stress and expense of dealing with an overheated engine. Remember, the key to preventing overheating is vigilance and timely action.
Want more videos all about auto?
Subscribe to our YouTube channel 👉Cartech Home